Abstract
Introduction: Currently, the standard of care for patients (pts) with relapsed/refractory (RR) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who relapse > 1 year after frontline treatment is salvage chemoimmunotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) in appropriately selected, chemosensitive pts. Following first-line therapy (tx) with a rituximab-containing anthracycline-based regimen in the modern era, response rates to platinum-based chemoimmunotherapy are suboptimal. More effective salvage regimens for RR DLBCL remain an unmet need. Polatuzumab vedotin (Pola) is an antibody-drug conjugate directed against CD79b that is safe and effective when combined with chemotherapy in frontline and relapsed, transplant-ineligible DLBCL pts [Tilly NEJM 2022, Sehn, JCO 2020]. We evaluated the safety and efficacy of Pola combined with rituximab, ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide (RICE) as second-line tx in RR DLBCL in a multicenter phase 2 study.
Methods: Adult transplant-eligible pts with ECOG ≤ 2 who had biopsy-proven RR DLBCL following frontline CD20-directed anthracycline-based chemoimmunotherapy were eligible. Pts with DLBCL not otherwise specified (NOS), transformed indolent lymphoma, primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma, high grade B-cell lymphoma (HGBCL) NOS, and HGBCL with MYC and BCL2 rearrangements were eligible. Pts with central nervous system lymphoma, peripheral neuropathy (PN) ≥ grade (gr) 2 or prior tx of RR DLBCL were excluded. Participants received PolaR-ICE: 1.8mg/kg Pola day (d) 1, rituximab 375mg/m2 d1, etoposide 100 mg/m2 IV d1-3, carboplatin AUC 5 (750 mg max) IV d2, ifosfamide IV 5000 mg/m2 d2 (inpatient) or divided between d1-3 (outpatient) every 21d for 2 cycles followed by PET-CT. G-CSF prophylaxis was mandatory. Pts in CR were eligible to proceed directly to ASCT or could receive a 3rd cycle of PolaR-ICE at investigator's discretion. Pts with partial response (PR) [or stable disease, MD discretion] received a 3rd cycle of PolaR-ICE. After ASCT, pts in ongoing response who had recovered from ASCT toxicities were eligible to receive Pola consolidation (1.8mg/kg) in 21d cycles starting d+30-60 to complete a cumulative 6 doses of Pola. A safety lead-in of up to 8 pts were enrolled according to the IQ rolling 6 design, with a de-escalation dose available (Pola 1.4mg/kg). Following the lead-in, a 2-stage design was employed with 20 pts enrolled (including lead-in) and since 8+ CRs were observed, the study proceeded to enroll a total of 40 pts. The co-primary endpoints were safety and CR rate according to 2014 Lugano classification. ORR, PFS and overall survival were secondary endpoints.
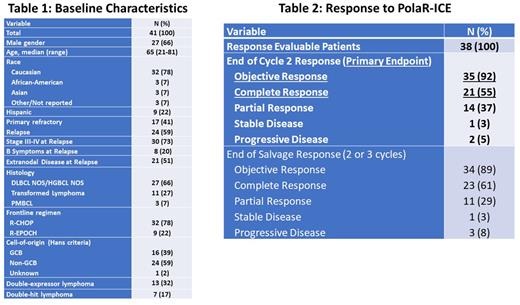
Results: 41 pts were enrolled; baseline characteristics are shown in Table 1. 37 pts were evaluable for response: 1 pt died prior to response assessment, 1 pt was inevaluable for response and replaced, 1 pt had clinical progressive disease (PD) and counted in ORR evaluation as PD, and 1 pt is pending response evaluation. 40 pts have toxicity data available, including 22 pts who received 3 cycles of PolaR-ICE, 16 treated with 2 cycles to date, and 2 pts who received 1 cycle to date. Of 38 pts (37 evaluable + 1 clinical PD), 35 had an objective response after 2 cycles of PolaR-ICE for an ORR of 92%, 21 (55%) had a CR, 14 (37%) had a PR, 1 had stable disease and 2 had PD. The end of salvage (PolaR-ICE x 2 or 3) ORR was 89% and CR rate 61% (1 PR became PD and 2 PR converted to CR with a 3rd cycle). To date, 21 pts proceeded to ASCT and 13 pts received consolidation Pola. The most common treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAE, all gr) related to PolaR-ICE were anemia (78%), nausea (70%), thrombocytopenia (70%), leukopenia (50%), fatigue (48%), neutropenia (48%), lymphopenia (38%), constipation (35%), hypertension (30%), and hypophosphatemia (28%). The most common gr ≥ 3 TEAEs were anemia (43%), thrombocytopenia (43%), neutropenia (43%), and no other non-hematologic TEAE occurred in more than 2 (5%) pts. 1 pt underwent Pola dose reduction due to gr 4 cytopenias, gr 2 nausea. Gr ≥ 3 infection/febrile neutropenia/sepsis occurred in 3 (8%) pts. 1 pt had a study treatment-related gr 5 AE due to sepsis. PN occurred in 10 (25%) pts, all gr 1 except one gr 2 event.
Conclusion: PolaR-ICE produced a high ORR with CR in a majority of pts and the safety profile was similar to RICE, without added toxicity due to Pola. Longer follow-up is needed to assess the durability of responses and outcomes following ASCT/Pola consolidation.
Disclosures
Herrera:KiTE Pharma: Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy; Tubulis: Consultancy; Adicet Bio: Consultancy; Regeneron: Consultancy; Genmab: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Caribou: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Merck: Consultancy, Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Karyopharm: Consultancy. Crombie:Kite: Consultancy; Roche: Research Funding; Bayer: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy. Cohen:Aptitude Health: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Novartis: Research Funding; Kite Pharma/Gilead: Consultancy; Lilly Oncology/Eli Lilly: Consultancy, Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Astrazeneca: Consultancy, Research Funding; HutchMed: Consultancy, Research Funding; BeiGene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; BMS/Celgene: Research Funding. Advani:ADC Therapeutics, Cyteir, Daiichi Sankyo, Gilead, Merck, Regeneron, Roche, Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics, BMS, Daiichi Sankyo, Epizyme, Gilead, Incyte, Merck, Roche, Sanofi: Consultancy. LaCasce:Research to Practice: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy. Godfrey:Merck: Research Funding; Secura Bio: Research Funding. Shouse:Kite Pharma: Speakers Bureau; Beigene Inc USA: Honoraria. Mei:Incyte/Morphosys: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Honoraria; CTI: Honoraria; BMS: Research Funding; Beigene: Research Funding; EUSA: Honoraria. Rosen:Pheromone Bio, Inc: Consultancy; Exicure: Consultancy; Apobiologix/Apotex Inc: Consultancy; PharmaGene, LLC: Consultancy; Trillium Therapeutics, Inc: Consultancy; Verastem, Inc: Consultancy; NeoGenomics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pepromene Bio, Inc: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pepromene Bio, Inc: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; Exicure: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; January Biotech: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; Trillium Therapeutics: Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company. Matasar:ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria; Juno Therapeutics: Consultancy; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; ImmunoVaccine Technologies: Honoraria, Research Funding; GlaxoSmithKline: Honoraria, Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Rocket Medical: Consultancy, Research Funding; Merck: Consultancy, Current equity holder in private company; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy; IMV Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria; Epizyme: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria; Bayer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Genentech, Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Teva: Consultancy; IGM Biosciences: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Consultancy.
OffLabel Disclosure:
Polatuzumab vedotin is approved after 2 prior therapies in the US, is approved as frontline therapy for DLBCL in Europe.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal